A solid data backup and recovery strategy is more than just a plan for copying files. It's your blueprint for survival, outlining exactly how you'll get your data back online after a disaster. These plans are what guarantee business continuity, minimizing the downtime and financial bleeding that come with any major incident.
Think of it less as a simple backup and more as a complete resilience system, ready to stand up against hardware meltdowns, cyberattacks, and even the classic "oops, I deleted that" human error.
Why a Resilient Recovery Strategy Is Non-Negotiable

Let's be blunt: data loss isn't a question of 'if,' it's a question of 'when.' In a world where your entire operation hinges on constant access to data, treating backups as just another line item on the IT budget is a recipe for failure. A robust recovery plan isn't a cost center; it's a core pillar of your business and a real competitive advantage.
The threats you're facing are more diverse than ever. We all worry about hardware failures, but what about the silent killers? Things like gradual data corruption can go unnoticed for weeks, quietly poisoning your backups. And of course, there's always the human element—one accidentally deleted database or a misconfigured script can bring everything to a grinding halt.
The True Cost of Downtime
The financial hit from an outage is what most people see first, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg. The real damage often runs much deeper and sticks around for a lot longer.
- Erosion of Customer Trust: When your platform is down, customer confidence evaporates. They count on you to be available, and a long outage is the fastest way to send them looking for a more reliable alternative.
- Brand Reputation Damage: Bad news travels fast, especially news about data loss or major service interruptions. The hit to your reputation can take years to repair, impacting future sales and partnerships.
- Operational Paralysis: It’s simple—without access to critical data, your team can’t work. Supply chains freeze, decisions are put on hold, and the entire business stalls.
A reactive approach to data recovery is a failing one. By the time a disaster strikes, it's too late to build a plan. Proactive, strategic planning is the only way to ensure modern business resilience.
A Growing Market Underscores the Urgency
This shift from a reactive to a proactive mindset is clearly reflected in the market. The global data backup and recovery market was valued at around $29.2 billion in 2024 and is expected to explode to $88.9 billion by 2035. This massive growth is driven by two key factors: ever-increasing data volumes and a constant rise in cybersecurity threats.
With the persistent threat of ransomware, a rock-solid recovery strategy is absolutely critical. Today’s sophisticated attacks don’t just steal data; they actively hunt down and encrypt your backup files to cut off your only escape route. This makes a resilient, multi-layered approach essential for defending your organization against ransomware attacks.
Waiting for an incident to see if your defenses hold up is a gamble you really can't afford to lose.
Getting the Foundations Right
Before you can build a bulletproof backup plan, you need to speak the language. A truly effective data recovery strategy isn't just about buying software; it's built on a few core ideas that will shape every decision you make, from technology choices to your budget. Nailing these fundamentals is the first real step toward a plan that won't let you down when things go sideways.
At the center of it all are two critical metrics: the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and the Recovery Point Objective (RPO). These aren't just technical terms—they're business decisions with very real consequences.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): This is your line in the sand for downtime. It’s the absolute maximum time you can afford for your systems to be offline after a disaster. If your RTO is one hour, you need to be fully operational again within 60 minutes. A lower RTO is always better, but it usually comes with a bigger price tag and more complex tech.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): This number defines how much data you can stand to lose, measured in time. An RPO of 15 minutes means that in a worst-case scenario, you can't lose more than the last 15 minutes of work. This metric is what dictates how often you need to run your backups.
Here’s the simple way to think about it: RTO is all about how fast you need to get back online. RPO is about how much data you can afford to lose for good. Defining these two numbers is the single most important thing you'll do.
Choosing Your Backup Method
Once you have your RTO and RPO locked in, you can start looking at the how—the actual type of backup you'll run. Each method strikes a different balance between how fast the backup runs, how much storage it eats up, and how painful the restoration process is.
To make sense of the options, it helps to see them side-by-side.
Comparing Full, Incremental, and Differential Backups
| Backup Type | Backup Speed | Storage Usage | Restoration Speed/Complexity | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Backup | Slowest | Highest | Fastest / Easiest | Initial backups, weekly archives, or when storage is not a concern. |
| Incremental | Fastest | Lowest | Slowest / Most Complex | Daily backups of critical, frequently changing data to save space. |
| Differential | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate / Simpler than Incremental | A balanced approach for daily or frequent backups with faster restores. |
A full backup is exactly what it sounds like: it copies everything, every single time. It’s dead simple to restore from but incredibly slow and a total storage hog.
An incremental backup is much smarter, only grabbing the data that has changed since the last backup of any type. This makes it quick and light on storage. The trade-off? Restoring can be a complex puzzle, as you might need the last full backup plus every incremental one since.
A differential backup offers a nice middle ground. It copies all the data that has changed since the last full backup. It takes up more space than an incremental but is much simpler and faster to restore.
The Power of the 3-2-1 Rule
There’s a time-tested framework in the data world that dramatically cuts down the risk of losing everything: the 3-2-1 rule. It's a simple, powerful principle that builds redundancy into your strategy, protecting you from almost any single point of failure.
Here’s how it works. You should always have:
- Three total copies of your data (your primary data plus two backups).
- Store those copies on two different types of media (like an on-site server and cloud storage).
- Keep one of those copies completely off-site to guard against physical disasters like fire, flood, or theft.
Following this rule means that if your production data gets hit with ransomware, you have a local backup ready to go. If a fire takes out your entire office, your off-site cloud copy is safe and sound. It’s a foundational piece of any serious data protection plan, and we follow similar principles in our own data handling, as outlined in our privacy policy.
The chart below shows just how much your backup frequency—which is driven by your RPO—can impact the risk of a major data loss.
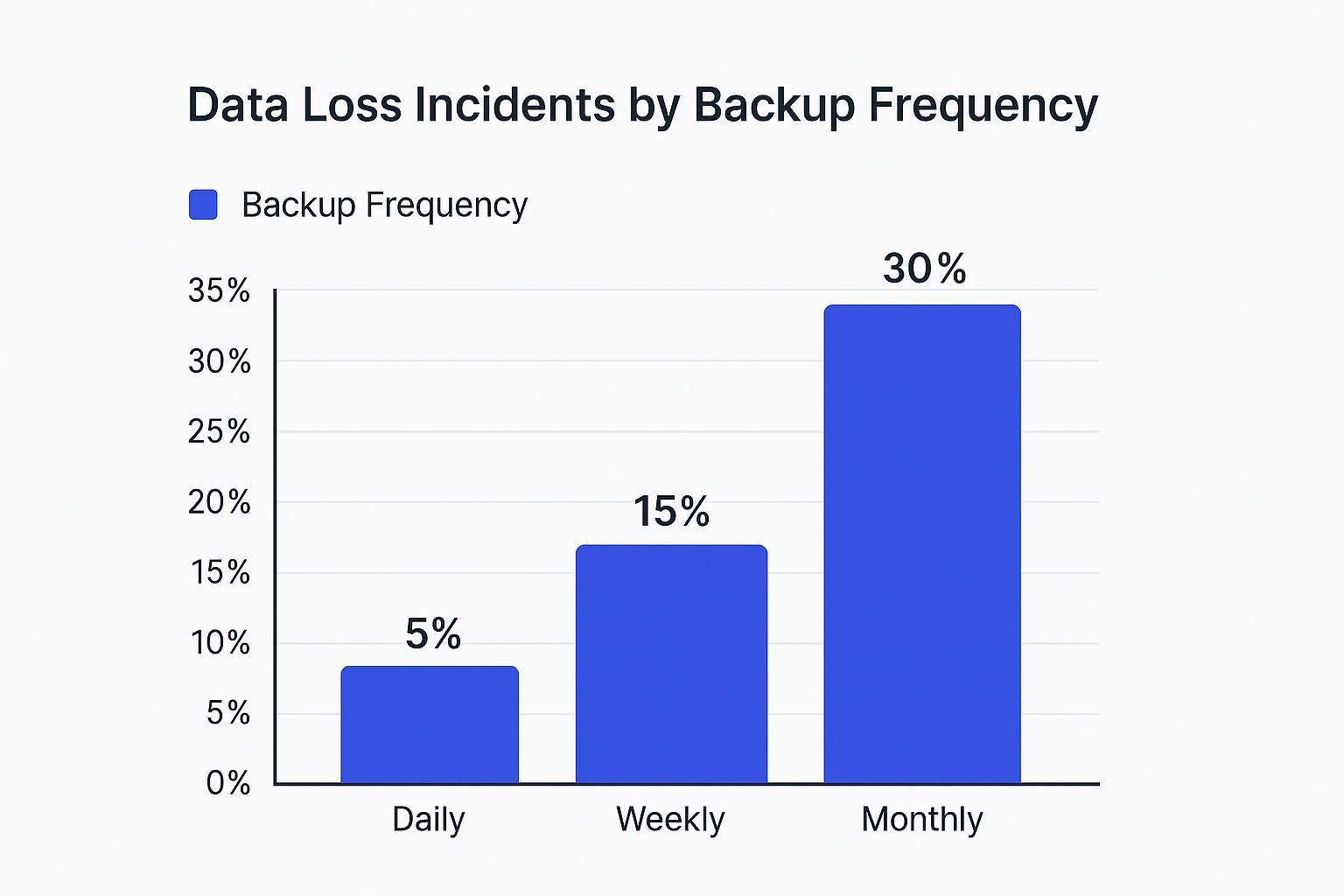
It’s pretty clear: shrinking the time between backups from monthly to daily isn't just a small tweak. It fundamentally reduces your exposure to a catastrophic data loss event.
Choosing the Right Backup Solution for Your Business
Once you've got the basics down, it's time to pick your tools. The market is flooded with options, and every single one promises to be your data's knight in shining armor. Your job is to cut through that noise and find a solution that actually fits how you operate, what regulations you're up against, and of course, your budget.
This choice really comes down to three flavors: the old-school on-premises hardware, the popular cloud-based Backup-as-a-Service (BaaS), or a hybrid model that tries to give you the best of both. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer here. The right choice is completely dependent on your specific situation.
On-Premises Backup Solutions
This is the classic, hands-on approach. You own and manage everything yourself—the servers, the storage, the software. Your IT team is responsible for every last bit of it, from initial setup to troubleshooting when things go wrong.
- The upside? Complete, unadulterated control over your data. For some organizations, especially those with strict data sovereignty or compliance rules, this is non-negotiable. Plus, initial backups and restores can be lightning-fast since they're all happening on your local network.
- The downside? The initial price tag can be a real gut punch. You're also on the hook for all the ongoing maintenance, hardware upgrades, and figuring out how to scale as your data piles up. It can quickly become a massive operational headache.
Cloud-Based Backup as a Service (BaaS)
With BaaS, you're essentially subscribing to a service that handles all the messy details for you. Your data gets backed up straight to the provider's secure cloud infrastructure. For a lot of modern companies, especially startups and SMBs, this has become the go-to option.
The biggest win here is simplicity. You wipe out the need for a big capital investment in hardware and hand off the day-to-day management to experts. This frees up your own tech folks to focus on growing the business instead of just keeping the backup servers online.
For a fast-growing tech startup, a pure cloud solution is often the most logical choice. It offers immense scalability on demand without the headache of provisioning new hardware, allowing the business to grow without technical limitations.
The pay-as-you-go pricing is another massive draw. You can easily scale your storage up or down whenever you need to, which makes it an incredibly flexible and cost-effective route. This aligns perfectly with the kind of flexible subscription models you see in our own Olostep pricing plans.
Hybrid Backup Models
A hybrid strategy is all about getting the best of both worlds. Typically, this means you keep a local backup on-site for quick, everyday recoveries, but you also replicate that backup to the cloud. That cloud copy is your ace in the hole for major disasters and long-term storage.
This approach is a direct application of the 3-2-1 rule, giving you both a local copy and a safe, off-site one. It's becoming incredibly popular for businesses that need the speed of local restores but also want the security and geographic separation that the cloud offers. Think of a healthcare provider with strict HIPAA rules—they might use a hybrid model to keep recent patient data on-site for fast access while archiving older records securely in a compliant cloud.
Making the Right Choice for Your Industry
Your industry often sets the tone for your backup strategy. In highly regulated fields like Banking and Finance (BFSI), a staggering 85% of organizations run daily backups, and 90% have a formal disaster recovery plan. The tech sector isn't far behind, with 80% backing up daily. Those numbers tell a clear story: the more red tape you face, the more robust your data protection needs to be. You can dive deeper into these trends in this backup statistics report.
To help you sort through the options, here’s a quick breakdown of how they stack up.
| Factor | On-Premises | Cloud (BaaS) | Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost Structure | High upfront CAPEX, ongoing OPEX | Subscription-based OPEX | Balanced CAPEX and OPEX |
| Scalability | Limited; requires hardware purchase | High; nearly infinite on-demand | High; scales with cloud component |
| Management | Full internal responsibility | Managed by provider | Shared responsibility |
| Restore Speed | Very fast for local data | Slower; dependent on bandwidth | Fast local, slower cloud |
| Security Control | Full physical and logical control | Provider-managed, shared model | High control locally, shared in cloud |
Ultimately, you need to take a hard look at the total cost of ownership, your team's technical skills, and what you actually need to achieve with your recovery plan. The right solution will support your business goals without turning into a financial black hole or an operational nightmare.
Crafting Your Actionable Recovery Plan
This is where the rubber meets the road. A brilliant backup strategy is just a piece of paper if your team can’t actually execute it when the pressure is on. A formal, actionable recovery plan is what turns your goals into a concrete, step-by-step playbook that takes all the guesswork out of a crisis.
The whole process starts with a simple truth: you can't protect what you don't know you have. Before you can think about schedules or who does what, you need a crystal-clear picture of your entire data landscape.
Conduct a Data Inventory and Impact Analysis
First things first, you need a thorough data inventory. This isn't just about listing servers; it’s about mapping out your entire data ecosystem. You have to identify every critical piece of data your startup runs on, where it lives, who’s in charge of it, and how it moves between your systems.
Once you have that map, you can get to the real meat of the issue with a Business Impact Analysis (BIA). The BIA is how you connect specific data to actual business functions. It answers the one question that matters most: "So what if this data is gone?"
- Identify Your Crown Jewels: Pinpoint the applications and datasets that are absolutely non-negotiable for your day-to-day operations.
- Put a Price on Downtime: For each of those systems, estimate the real financial and operational damage caused by an outage. What's the cost per hour if your primary database goes dark?
- Set Your Priorities: Use this analysis to rank your systems from most to least critical. This ranking is what will directly inform your RTO and RPO targets, making sure you throw your most aggressive recovery efforts where they’ll make the biggest difference.
A classic rookie mistake is treating all data as equally important. Your marketing blog and your core customer database do not need the same recovery speed. A BIA gives you the objective logic to put your resources where they count.
Defining Policies and Procedures
With a solid understanding of what your data is worth, you can now build the core policies that will govern your recovery plan. These aren't just gentle suggestions—they're the documented rules of the road for data protection.
Here are the key policies you need to nail down:
- Backup Schedules: Based on your RPO, define exactly how often each type of data gets backed up. Critical transaction logs might get backed up every 15 minutes, while less volatile application servers could be backed up daily.
- Data Retention Policies: Decide how long you need to keep your backups. This is often driven by compliance rules (like HIPAA or GDPR) but also by your own business needs. A common approach is keeping daily backups for a week, weekly backups for a month, and monthly backups for a year.
- Encryption Protocols: Be specific about the encryption standards for data both in-transit (as it’s moving to backup storage) and at-rest (while it’s sitting there). For any sensitive information, this is completely non-negotiable.
Documenting Recovery Steps and Assigning Roles
This is arguably the most important part of the entire plan. When an incident is unfolding, adrenaline is pumping, and nobody has time to think. Clear, unambiguous instructions are everything. You must document the exact, step-by-step procedures for restoring your different systems.
Your documentation needs to be so clear that an engineer with the right skills—but zero prior knowledge of your setup—could follow it. That means including server names, login credentials (stored securely, of course), and the specific commands or UI clicks needed to kick off a restore.
Just as critical is assigning clear roles and responsibilities. Your plan has to name names.
- Who has the authority to declare a disaster? There needs to be a clear chain of command.
- Who is responsible for bringing the primary database back online?
- Who handles all communication with stakeholders, partners, and customers?
- Who gets the final say on whether the recovery was successful?
Without pre-defined roles, a crisis descends into chaos, with people tripping over each other or, worse, assuming someone else is handling it. A well-defined team ensures everyone knows their job and can get it done fast. For a fantastic framework to build on, check out this guide to a modern IT disaster recovery plan.
The Essential Recovery Plan Checklist
Think of your final document as a living, breathing guide that grows with your business—it's not a "set it and forget it" task. As you put your plan together, make sure it covers these essential bases.
| Component | Description | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Contact Information | An up-to-date list of all recovery team members, key stakeholders, and external vendors with personal cell numbers. | When a major outage hits, your usual channels like email or Slack might be completely offline. |
| Activation Criteria | The specific conditions that officially trigger the recovery plan. | This prevents people from jumping the gun or waiting too long, providing clear authority to act now. |
| Step-by-Step Procedures | Detailed, idiot-proof instructions for restoring each critical system, laid out in the proper sequence. | It drastically reduces human error under pressure and makes the entire recovery process faster. |
| System Dependencies | A map that shows how different systems and applications rely on one another. | This ensures you restore things in the right order (e.g., identity management before business apps). |
| Location of Backups | Precise details on where your backup data is stored, including cloud storage credentials or physical safe locations. | You can't restore data you can't find. This info has to be immediately accessible to the team. |
By meticulously building this plan, you graduate from just having backups to having a true recovery capability. This document is your team's lifeline, ensuring that when a crisis hits, your response is organized, efficient, and—most importantly—successful.
Testing and Maintaining Your Recovery Readiness
An untested backup is just a hope. You can architect the most brilliant recovery plan on paper, but if it's just sitting on a shelf collecting dust, it's worthless when a real crisis hits. This is where the real work begins.
The final, critical phase is all about building confidence through disciplined testing and maintenance. You need to know, without a shadow of a doubt, that your plan will hold up under pressure. This means treating your recovery strategy not as a one-and-done project, but as a living part of your daily operations.
From Simple Drills to Full Simulations
Testing isn't a single, monolithic event. It’s a spectrum of activities, each designed to validate a different piece of your recovery puzzle. You don’t have to simulate a full-blown catastrophe every month. A layered approach is far more practical and ensures everything gets checked regularly without constant disruption.
- File Restore Drills (Monthly): This is your bread and butter. Every month, randomly pick a few non-critical files or a small database from a recent backup and restore them to a test environment. The goal is simple: prove the backups aren't corrupted and the basic restore process actually works.
- System Recovery Tests (Quarterly): Time to level up. Restore an entire server or a critical application into an isolated sandbox. This tests more than just the data; it validates application dependencies and configurations, ensuring you can bring a full system back online from scratch.
- Tabletop Exercises (Bi-Annually): Get the whole recovery team in a room. Walk through a disaster scenario on paper, step-by-step. Talk through every decision, from initial detection to the final all-clear. These exercises are invaluable for finding gaps in communication, clarifying roles, and spotting logical flaws in your procedures before they bite you.
- Full Disaster Simulation (Annually): This is the ultimate stress test. It involves failing over a critical system to your secondary site or cloud environment. Yes, it’s disruptive and resource-intensive, but it’s the only way to be 100% certain your entire end-to-end process works in the real world.
An annual, full-scale simulation might seem like overkill, but it's the only true validation of your Recovery Time Objective (RTO). It forces you to live through the recovery process, revealing every hidden bottleneck and assumption that could derail you during a real event.
The Unskippable Maintenance Checklist
Alongside testing, you need a routine maintenance schedule. This keeps your backup system healthy, secure, and aligned with your ever-changing tech stack. Skipping these simple checks is one of the most common reasons recoveries fail.
A clear schedule for these tasks is a must. Many teams track their status and performance right from their primary operations hub. For our users, you can monitor and manage these kinds of recurring tasks directly from the Olostep dashboard.
What to Monitor and Maintain
| Task | Frequency | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Monitor Backup Job Success | Daily | A single failed backup job can create a critical gap in your recovery timeline. You absolutely need automated alerts for any failures. |
| Review Storage Capacity | Weekly | Running out of storage is a rookie mistake that can halt your entire backup strategy. Keep an eye on trends and plan for growth. |
| Verify Backup Integrity | Monthly | This is how you catch "silent corruption"—when a backup looks successful but the data is unusable. Checksums and integrity checks are your best friends here. |
| Review User Access | Quarterly | A key security measure. Make sure only authorized personnel have access to your backup systems and data to protect against insider threats. |
| Update the Recovery Plan | Annually | Your business is always changing. New systems come online, old ones are retired. Your plan has to evolve to reflect your current environment. |
By embedding these testing and maintenance routines into your operational rhythm, you move from hoping you're ready to knowing you are. You build muscle memory within your team and gather hard proof that your data backup and recovery strategies are ready for anything.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Even the best-laid plans can leave you with a few lingering questions. Let's tackle some of the most common ones that pop up when teams are building out their data backup and recovery strategies.
What’s the Real Difference Between Backup and Disaster Recovery?
People often use these terms interchangeably, but they are fundamentally different things. It's a classic "square is a rectangle, but a rectangle isn't a square" situation.
Data backup is the act of making a copy of your data and storing it somewhere safe. Lost a critical file? Corrupted a database? You restore it from your backup. It's a specific, tactical action.
Disaster recovery (DR), on the other hand, is the entire strategic playbook. It’s the comprehensive plan that outlines exactly how your business gets back on its feet after a major incident—think server failure, ransomware attack, or even a natural disaster. DR includes your backups, but it also covers the people, processes, and technology needed to restore your whole IT operation.
Think of it this way: a backup is like having a spare tire in your trunk. A disaster recovery plan is your AAA membership, a map, and a mechanic on speed dial. One solves a specific problem; the other gets you through the entire crisis.
How Often Should We Be Backing Up Data?
This isn't a one-size-fits-all answer. The right frequency comes down to one critical question: how much data can you afford to lose forever? This is what we call your Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
The schedule should be dictated by the data itself.
- Continuous / Near-Continuous: For mission-critical systems where data changes every second—like your e-commerce platform's transaction logs—you need backups running constantly or every few minutes.
- Daily: This is the sweet spot for a lot of business data. Think application servers and team file shares. Losing up to a day's work is acceptable, if not ideal.
- Weekly: Some data is more static. Archived project files or servers that see infrequent updates might only need a weekly backup.
To figure this out for your own systems, you absolutely need to conduct a business impact analysis. It's the only way to properly classify your data and align your backup schedule with what the business actually needs.
Are Cloud Backups Actually Secure?
Yes, provided you choose a reputable provider. Major cloud backup services are built with security at their core, often offering a defense-in-depth approach that most startups could never afford to build themselves. We're talking end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest, plus adherence to tough compliance standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and HIPAA.
But here's the crucial part: it’s a shared responsibility model. The provider secures the cloud, but you have to secure your corner of it. That means enforcing multi-factor authentication, using strong access controls, and applying the principle of least privilege. Always do your homework on a provider's security credentials before handing over your data.
Data Loss Just Happened. What Are the First Steps?
Panic is your enemy. When an incident hits, a calm, methodical response is what will save you.
- Stop the Bleeding: Your first move is to contain the damage. Isolate the affected systems immediately. If it's a ransomware attack, this single step can prevent it from ripping through your entire network.
- Assess the Damage: Once the immediate threat is contained, you need to figure out exactly what was hit. Which systems? What data? This initial triage will guide your entire recovery effort.
- Sound the Alarm: It's time to officially declare an incident and activate your DR plan. Get your pre-assigned recovery team on the horn and let them know it's go-time.
- Start the Restoration: Follow your playbook. Begin restoring services based on the priorities you already defined in your business impact analysis. Critical systems first, always.
- Run a Post-Mortem: After everything is back online and stable, the work isn't over. You need to dig in and figure out the root cause. A thorough post-mortem is the only way to learn from the incident and strengthen your defenses to make sure it doesn't happen again.
Ready to build AI applications with reliable, structured data from any website? Olostep provides a powerful web scraping API that handles the complexity for you, delivering clean data in seconds. Start building smarter today.


